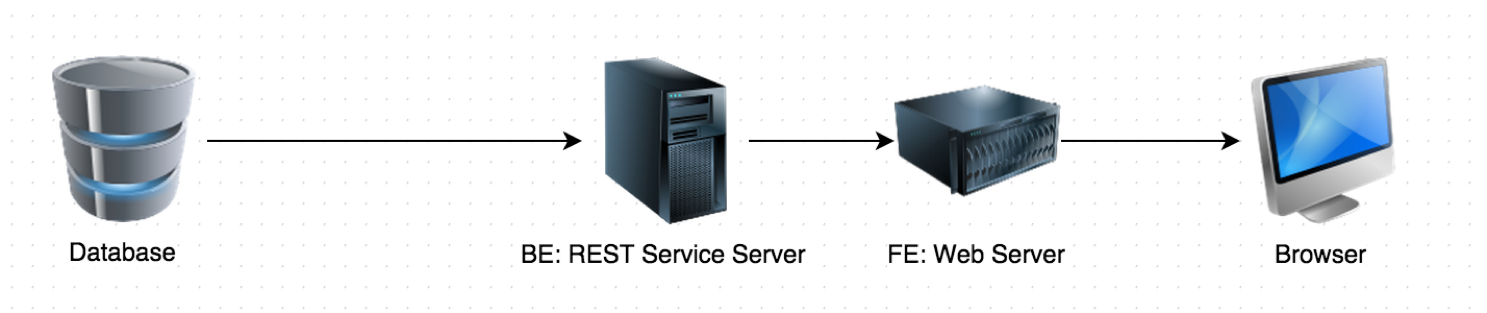
Simplify Complex Query with CQRS
Optimization is all about Resource Trade-off
The performance of an application is based on
- Memory Resource
- Computing Resource
- Network Resource
- Developer Resource
- Disk space Resource
Disk space resource is relatively the cheapest resource compared to others.
Example Requirement: Find Shipping Methods
- During checkout process, user will be presented a list of shipping methods to choose from, based on the product and shipping address.
- shippingMethods = findShippingMethodsBy(product, shippingAddress);
Example Requirement: Request Payload
Request Json Payload:
{
"productId": ”aabbcc",
"address": ”123 Freedom Cir., Santa Clara, CA 95123"
}
Common Strategy: Back-end Processing
- Upon receiving request payload:
// step 1: construct hierarchical object graph, an expensive operation. product = productRepository.findBy(productId); shippingAddress = new Address(address); // step 2: find shipping methods. shippingMethods = findShippingMethodsBy(product, shippingAddress);
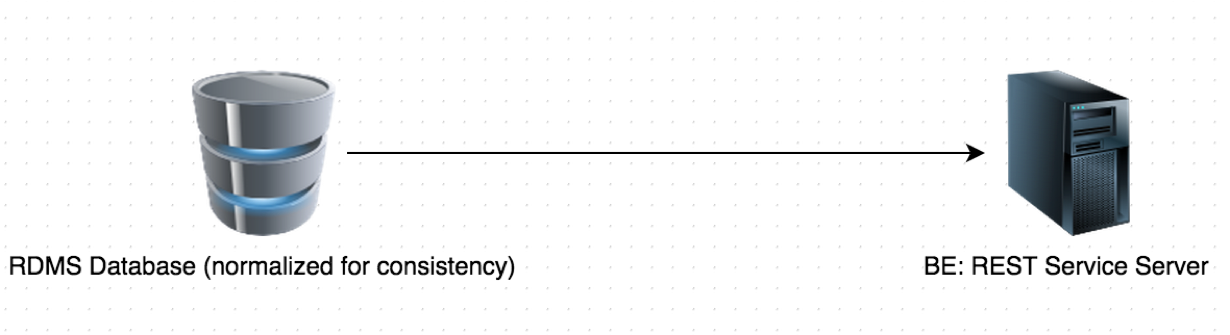
Common Strategy: ER Diagram
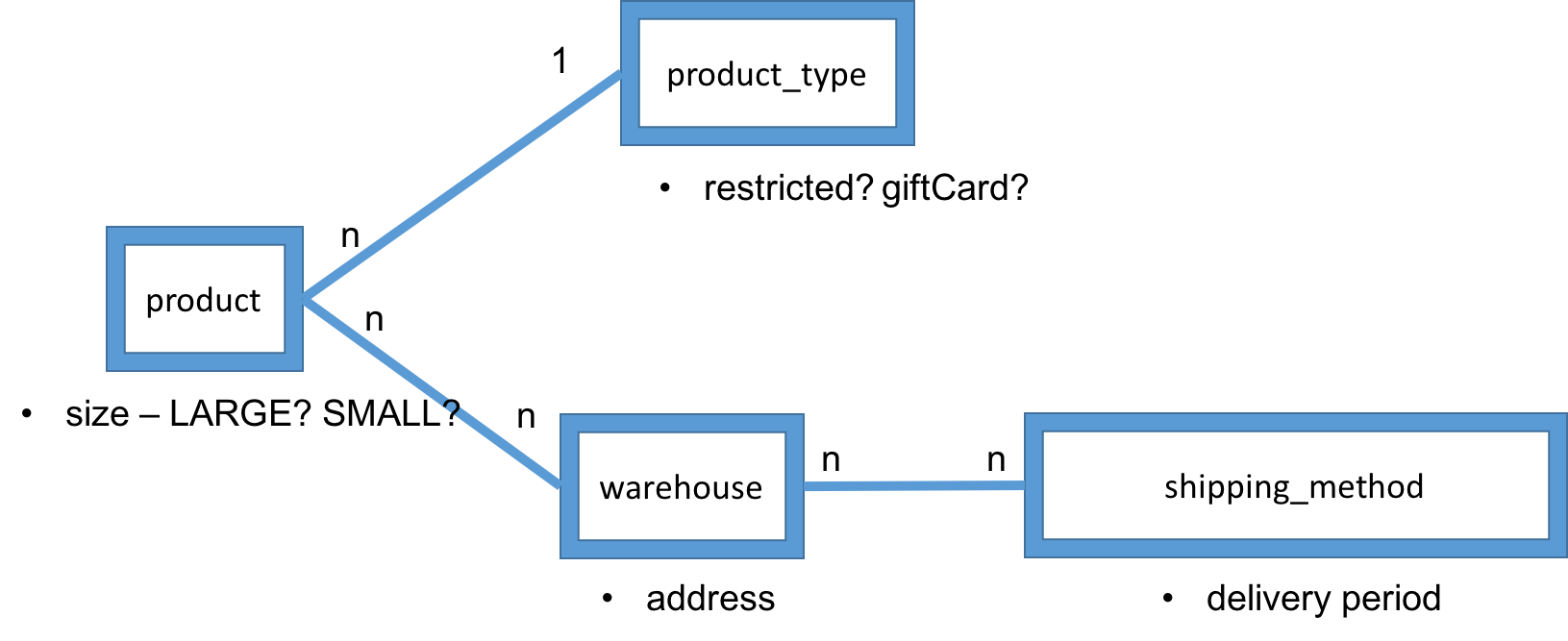
Common Strategy - Modeling
Model with Hierarchical Data object, e.g.
- Product
- size (LARGE, SMALL)
- type (GIFT_CARD, RESTRICTED)
- warehouses
- address
- shipping methods
- Shipping Address
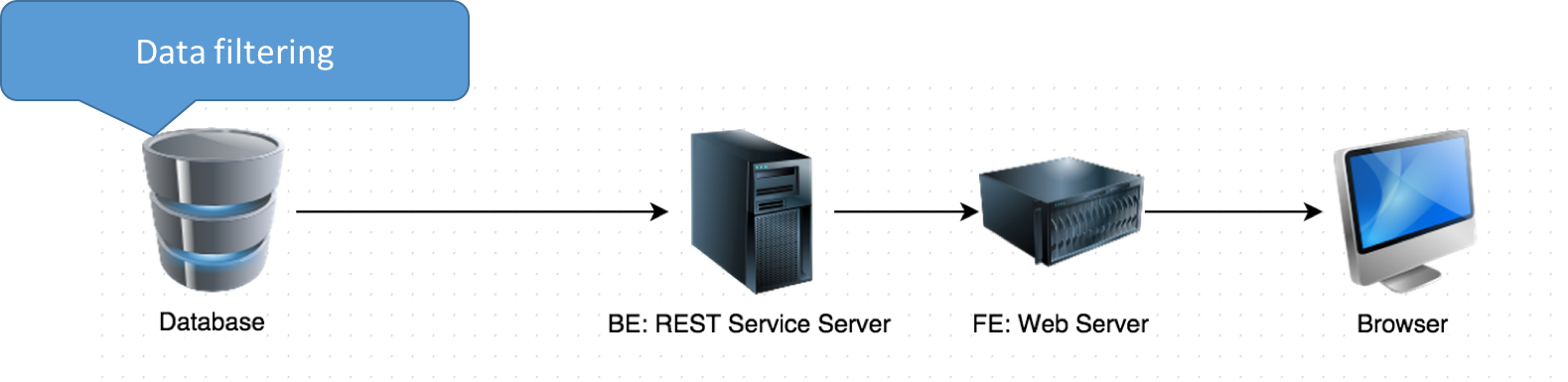
Issue #1: Network Traffic Increment.
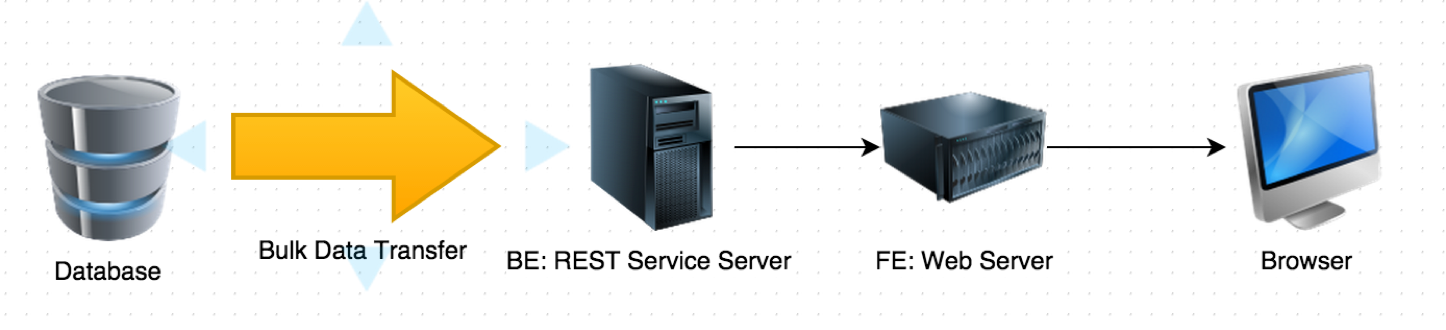
- For each request, application layer has to fetch huge amount of data across network from database, and process the data at Application layer.
Question: Which is the best layer to filter data?
Issue #2: Read Speed or Write Speed, Pick One.
- We cannot optimize both Read and Write speed at the same time.
- Without adding index,
- time complexity for read = O(n)
- After adding index,
- time complexity for read = O(log n)
Issue #2: Read Speed or Write Speed, Pick One. – Cont.
- Performance Summary from “The Performance Impact of Adding MySQL Indexes”
- For a table with 553875 rows.
| Before Adding Indexes | After Adding Indexes | |
|---|---|---|
| Insert Operation (sec) | 7.14 | 24.77 (3x) |
| Data (mb) | 33.56 | 33.56 |
| Index (mb) | 13.52 | 95.70 |
| Total = Data + Index (mb) | 47.08 | 129.27 |
Issue #2: Read Speed or Write Speed, Pick One. – Cont.
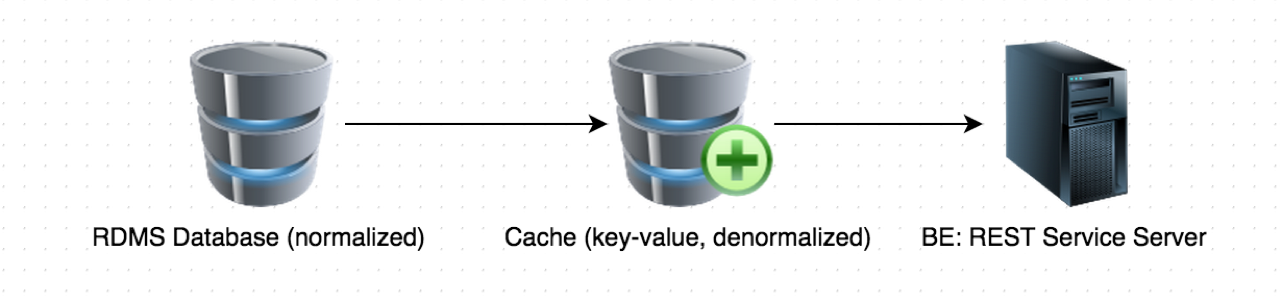
- What if we use Cache to reduce DB read?
- Cache is a Key-Value DB.
- Let’s say it takes 32 DB calls to build a complex object graph:
- Best case: 32 cache hits.
- Worst case: 32 cache misses + 32 DB calls.
-
Network IO delays is unavoidable.
- There is another challenge: Cache Data Consistency.
There are only two hard things in Computer Science: cache invalidation and naming things.
– Phil Karlton
Issue #2: Read Speed or Write Speed, Pick One. – Cont.
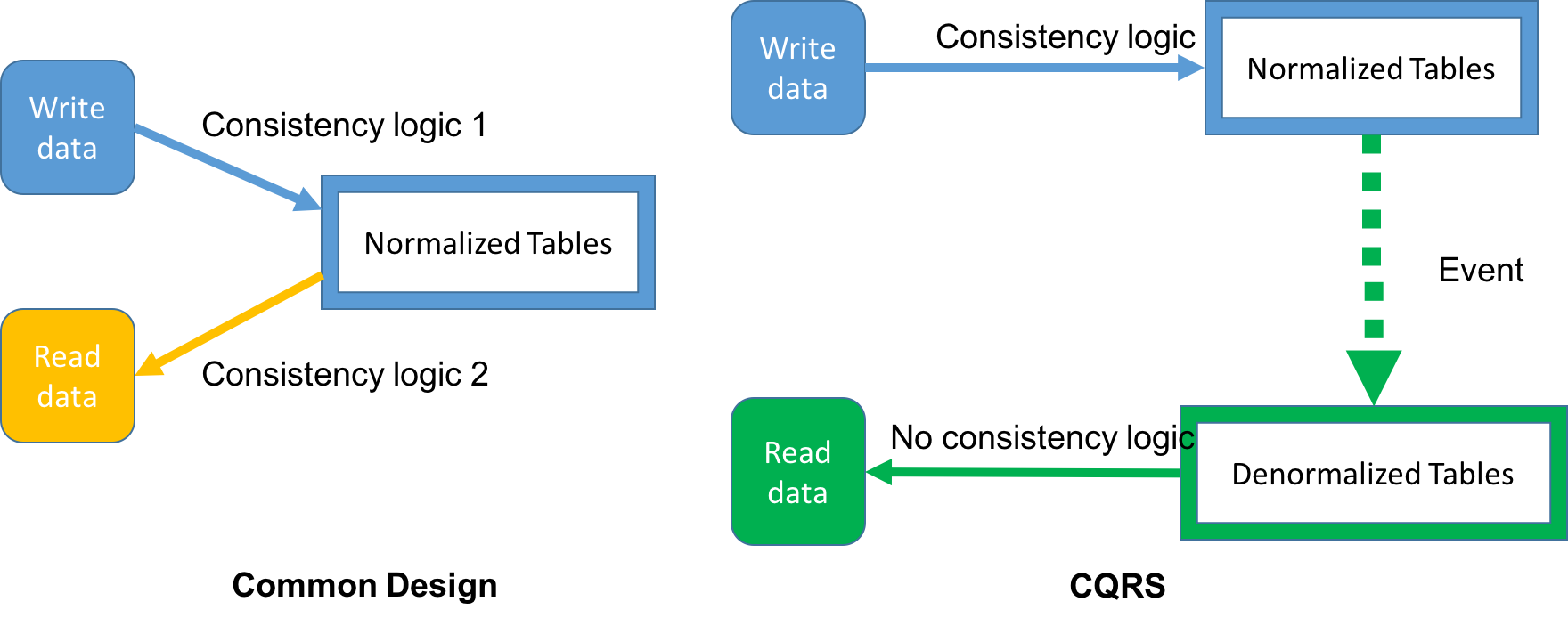
We need to maintain consistency for both normalized DB and denormalized DB, and this is tricky.
Overall Consistency = Consistency (Normalized) && Consistency (Denormalized)
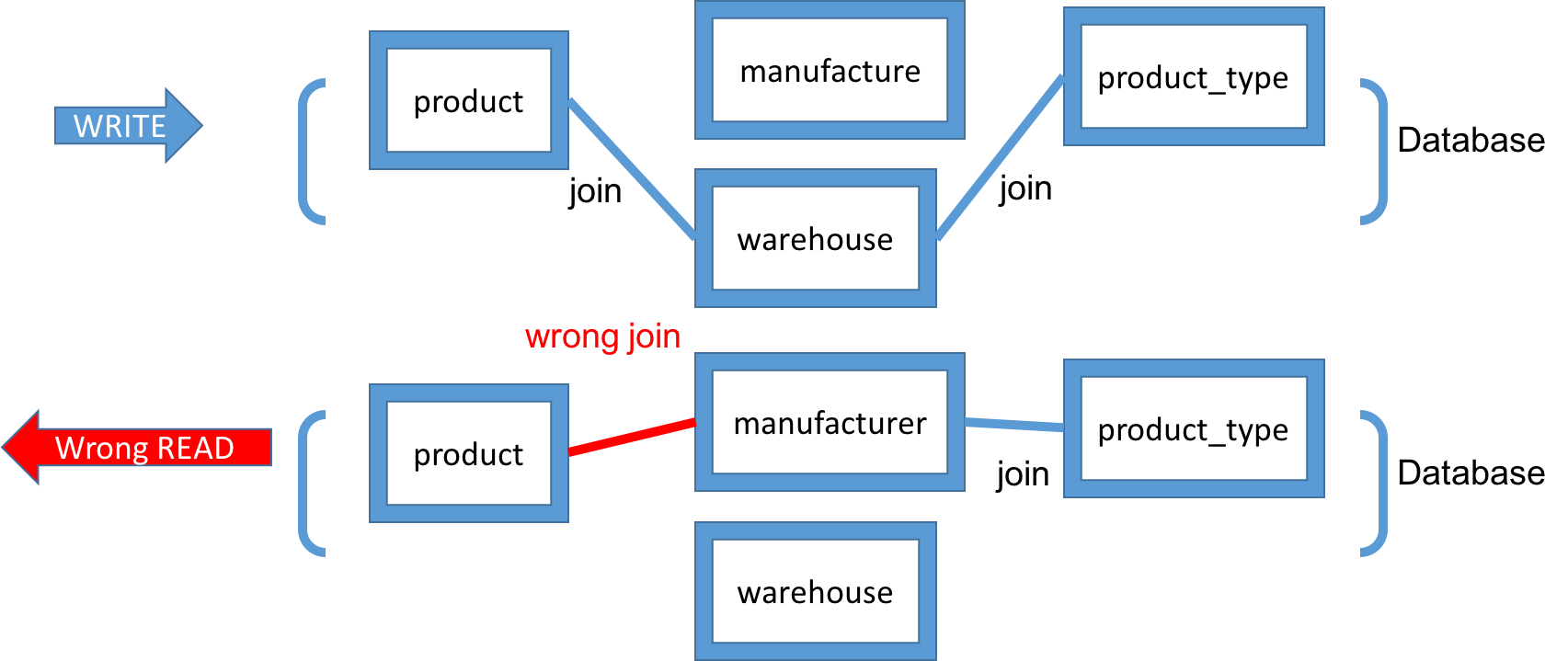
Issue #3: “Join” logic has to be at both sides (W, R)
CQRS Comes to Rescue.
- Proposed by Greg Young.
- Probably the best innovation from C# community to Java community.
- Command-Query Responsibility Segregation.
- Command -> Write
- Query -> Read
- Separate design for Write Operation and Read Operation.
- For Write, we want consistency.
- For Read, we want speed.
Common Strategy
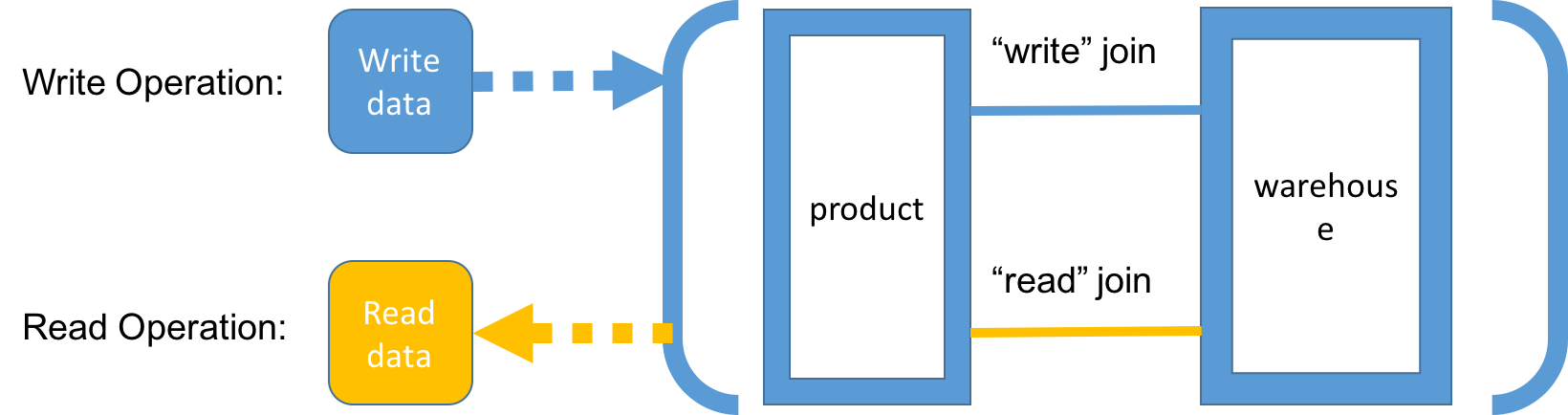
Read:
O(log n) if it is indexed correctly,
O(n) without index.
CQRS
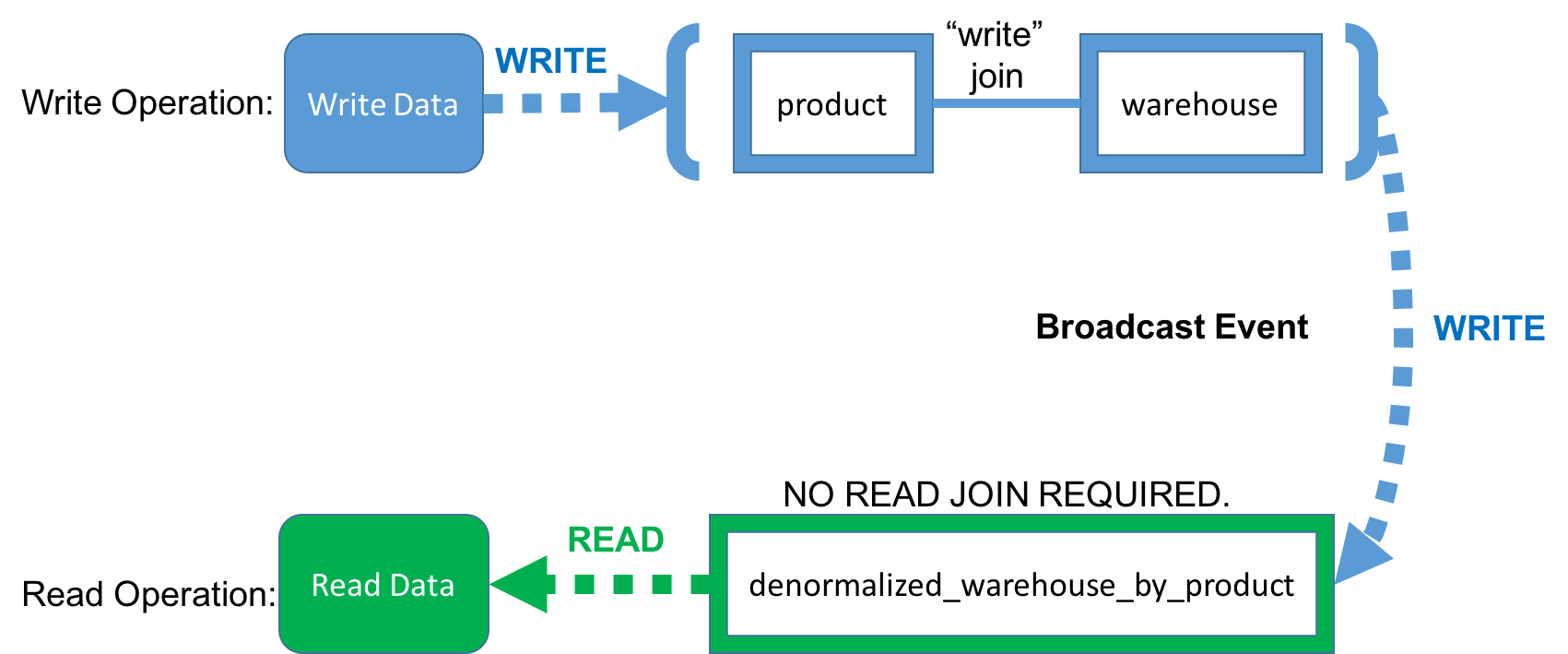
Benefit #1: Fast Read
- Simple read. No join operation.
- We can achieve O(1) time complexity by using appropriate database.
- Minimized data transfer – reduced network IO delay.
- Reduced memory requirement – reduced GC.
Benefit #2: Fast Write
- Less indexes created.
- Tables (for write operation) are not polluted by Indexes (which are created for read operation).
Benefit #3: Simple Read Logic
- Less convoluted Read-logic.
- Simple logic reduces mistakes.
- It promotes knowledge sharing among team members.
- Shorten development time.
Benefit #4: Flexibility - Different Databases
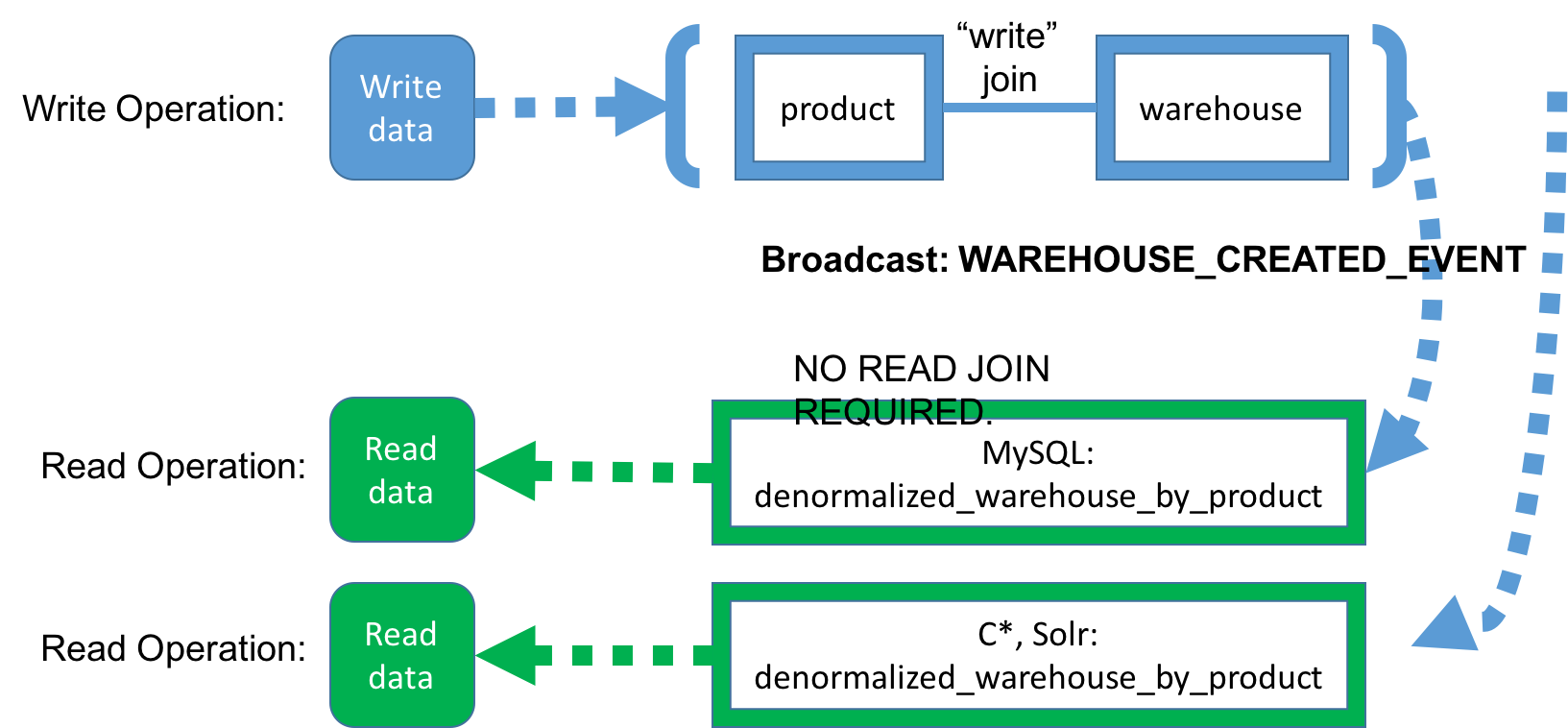
Benefit #5: Consistency